
MS SQL STRING_ESCAPE introduced in MS SQL 2016 escapes special characters in texts and returns text with escaped characters.
Syntax:
STRING_ESCAPE(text, type)
- Text - Is a string data type representing the object that should be escaped
- Type - Escaping rules that will be applied
The function returns the escaped text in nvarchar(max) data type.
Currently the only supported type of escaping rule is JSON.
JSON escaping rules:
- Quotation mark (") -> \"
- Reverse solidus (\) -> \\
- Solidus (/) -> \/
- Backspace -> \b
- Form feed -> \f
- New line -> \n
- Carriage return -> \r
- Horizontal tab -> \t
- Control characters (0-31) -> \u<code> (e.g. CHAR(0) -> \u0000)
Let’s see some examples.
Example:
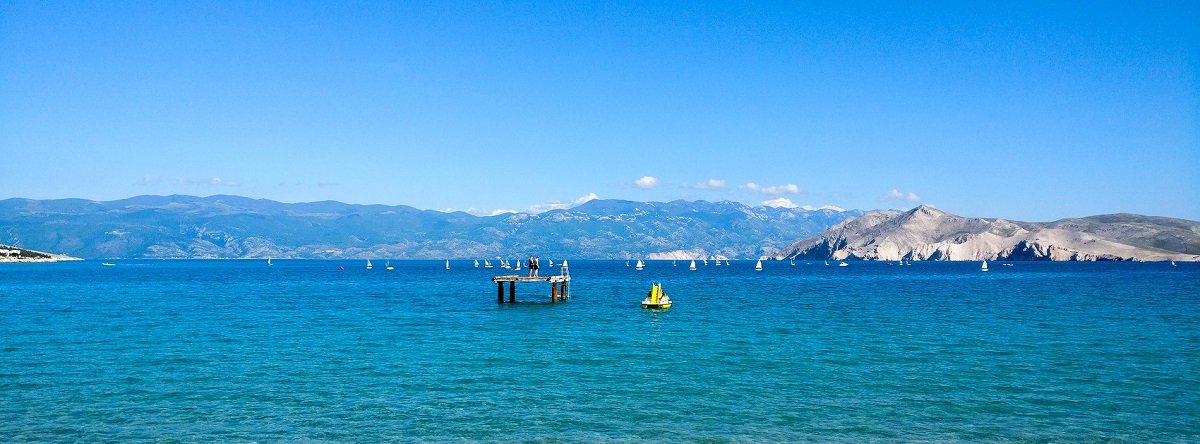
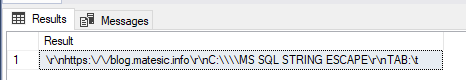
DECLARE @InputValue NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'
https://blog.matesic.info
C:\\MS SQL STRING ESCAPE
TAB: ';
SELECT STRING_ESCAPE(@InputValue,'JSON') AS Result;
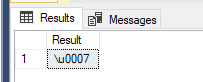
SELECT STRING_ESCAPE(CHAR(7),'JSON') AS Result;
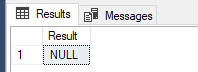
MS SQL STRING_ESCAPE returns NULL if the input value is NULL.
Example:
SELECT STRING_ESCAPE(NULL,'JSON') AS Result;
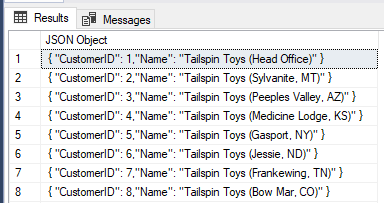
Let's try to create JSON objects based on real data from a table.
Example:
USE [WideWorldImporters];
SELECT
FORMATMESSAGE('{ "CustomerID": %d,"Name": "%s" }', [CustomerID], STRING_ESCAPE([CustomerName],'json')) AS "JSON Object"
FROM
[Sales].[Customers]
*MS SQL Server sample database "WideWorldImporters" can be downloaded at: https://github.com/Microsoft/sql-server-samples/releases/tag/wide-world-importers-v1.0
*You can download the complete SQL Script with all examples from the post here: SQL Script.sql (680.00 bytes)